Open Source in Enterprise – report 2022
We have analyzed the latest available reports on the use of open source software in enterprises. In this article, we provide a brief summary and key findings from this data.
We have analyzed the latest available reports on the use of open source software in enterprises. In this article, we provide a brief summary and key findings from this data.
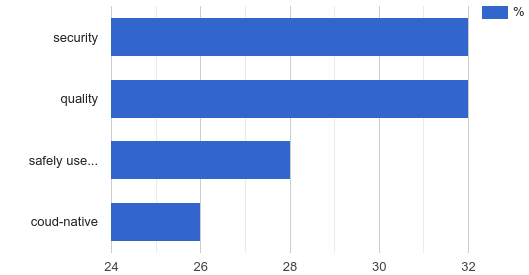
For IT managers, security is the main advantage of open source software – 89% of leaders believe that open source software is equally or more secure than closed source software. Anyone who has spent some time in the IT industry will see that this is a significant change from the mainstream perception of software a dozen years ago, when the security of Open Source software was often portrayed as a weak point.
IT leaders place their trust in the ways of developing and delivering Open Source software. Common answers to questions asked include: “security patches are well documented and easy to analyze” (one aspect of the software supply chain security) and “vendors are quick to provide patches for vulnerabilities in Enterprise Open Source software.” There is also the obvious argument that “more people have had insight into the code than with closed source software.” The ability to audit code internally is also an important factor.
Open source is an engine of innovation for the financial industry. In 2001, when we migrated from UNIX to Linux, we didn’t know we were changing our business. From standard foundations that increase productivity to the communities that foster the next frontiers of technology, open source opens doors to the future.
Why do company contributions to open source matter?
Respondents were overwhelmingly (more than 80%) more likely to choose software and service providers that contribute to the Open Source community.
The main reasons for preferring Open Source providers when choosing solutions are:
- they help maintain open source software
- they are familiar with open source processes
- they can influence the development of functions that enterprises need.
How are organizations using Open Source software?
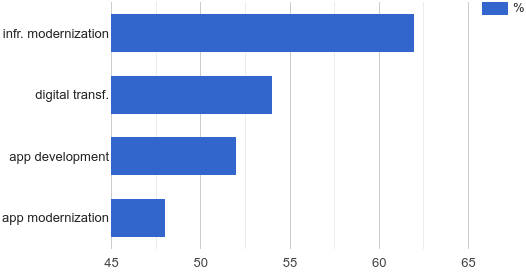
Infrastructure modernization has consistently been at the forefront of choosing open source solutions. In the past, this often meant that IT leaders got rid of closed-source software and introduced open-source software in its place.
These operations still take place, but there are also entirely new categories of software that did not previously exist to any significant degree in the closed-source software world.
Containers, Kubernetes for related container orchestration and the huge number of cloud-native open source projects may be the best examples of new software categories. This is a software ecosystem that is growing and shows no signs of slowing down. 70% of surveyed IT leaders work for organizations that use Kubernetes, and nearly a third plan to significantly increase their use of containers in the next 12 months.
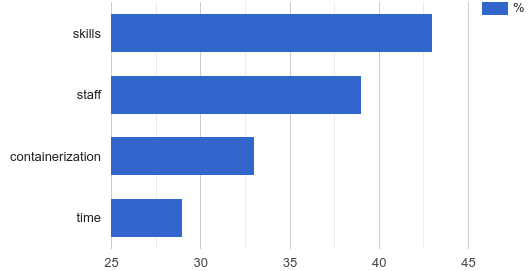
However, modernizing infrastructure (along with other leading open source applications) has its downsides. When asked about barriers to container implementation, the main obstacles varied somewhat by geographic region, but mostly included a lack of developers, general resources or necessary skills.
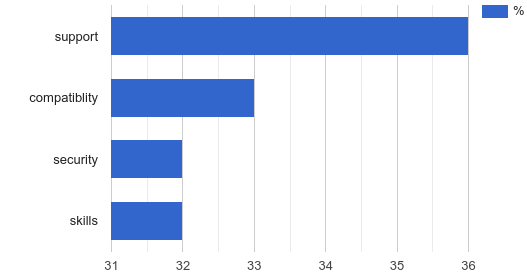
The main obstacles to the widespread adoption of Open Source in enterprises are more or less similar to the results of previous years. They include issues such as support levels, compatibility and security. They are very similar to the concerns IT managers hear about commercial closed-source software.
Linux, along with open source enterprise software in general, was adopted by companies largely because it offered a cheaper alternative to proprietary UNIX and closed network applications. Even as this view of corporate open source began to diverge more and more from reality, it remained a stereotype.
There has been a steady shift away from defining enterprise Open Source as cheaper and not better software. Of course, this doesn’t mean that Open Source software can’t be cheaper to buy and use than closed source software.
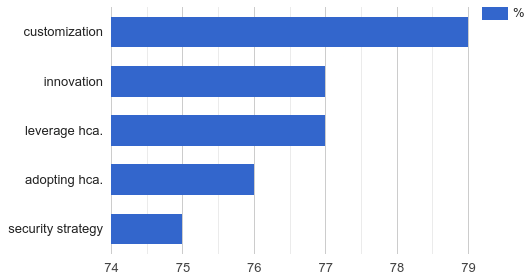
Open Source software provides flexibility, guarantees access to the latest innovations, plays a key role in the use of hybrid cloud architectures and is a key part of security strategies.
How has the perception of Open Source changed over the past year?
Unsurprisingly, the growing use of open enterprise software extends to important technology choices. 80% of respondents plan to increase their use of open source enterprise software in areas such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML) or edge computing and the Internet of Things (IoT).
A large proportion of IT managers surveyed see open source in an increasingly favorable light. An impressive 77% said they now have a more positive opinion of Open Source than they did just a year ago.
Summary
Open enterprise software continues to gain in popularity at the expense of closed software. Closed-source software, as a percentage of software already in use in organizations, is expected to drop eight points in the next two years. This is a huge decline. Over the same period, open enterprise software is expected to grow by five points, and open community software is expected to grow by three points. Enterprises can use well-tested open source code for corporate projects and it is becoming more common to use open source code in closed internal applications.
Sources:
https://www.redhat.com/en/resources/state-of-enterprise-open-source-report-2022
https://www.openlogic.com/resources/2022-open-source-report